Medical ear treatments, a specialized branch of otolaryngology known as otology, focus on diagnosing and managing disorders related to ear health. Otology encompasses the study and treatment of conditions affecting the ears, including hearing loss, infections, and structural abnormalities. Otolaryngologists specializing in otology play a crucial role in preserving and restoring ear function to optimize overall ear health and quality of life.
10 Types of Ear Treatments
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to treat bacterial ear infections. They work by inhibiting bacterial growth and eliminating the infection.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help reduce ear pain and inflammation.
- Ear Drops: Medicated ear drops are used to treat various ear conditions, such as swimmers’ ears, by reducing inflammation and fighting infections.
- Ear Irrigation: This procedure involves flushing out the ear canal with a gentle stream of water to remove excess earwax or debris.
- Ear Tubes: In cases of chronic ear infections or fluid buildup, small tubes may be inserted into the eardrums to facilitate drainage and ventilation.
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory medications can be used in some cases to reduce inflammation in the ear and alleviate symptoms.
- Earwax Removal: When earwax accumulates and causes discomfort or hearing difficulties, a healthcare professional may remove it using specialized tools or techniques.
- Tympanoplasty: This surgical procedure is performed to repair a perforated eardrum or reconstruct damaged middle ear structures.
- Mastoidectomy: In severe cases of chronic ear infections, a mastoidectomy may be necessary to remove infected bone in the mastoid process behind the ear.
- Cochlear Implants: For individuals with severe hearing loss, cochlear implants can restore some level of hearing by directly stimulating the auditory nerve.
Clinic contact number: +989371200167
Most Common Medical Ear Treatments
The most common medical ear treatments depend on the prevailing ear conditions in the population. Ear infections, particularly acute otitis media and otitis externa (swimmer’s ear), are frequent reasons for seeking medical attention. Antibiotics, ear drops, and pain relievers are often prescribed for these infections. Additionally, earwax buildup is a common concern, leading to the use of ear drops or irrigation to clear the ear canal.
Ear Infections (Otitis Media or External Otitis)
Ear infections are common conditions that can affect the middle ear (otitis media) or the outer ear canal (external otitis, also known as swimmer’s ear). Here are the typical treatments for each type of ear infection:
Antibiotics
Oral antibiotics or antibiotic ear drops are prescribed to treat bacterial ear infections.
Pain Relief
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen help alleviate ear pain and inflammation.
Warm Compress
Applying a warm compress to the affected ear can provide relief from discomfort.
Earwax Buildup (Cerumen Impaction)
- Ear Drops: Using over-the-counter ear drops to soften the earwax, facilitating its natural expulsion.
- Irrigation: Flushing the ear canal with warm water using a bulb syringe or irrigation kit to remove excess earwax.
- Manual Removal: Healthcare providers may manually remove impacted earwax using specialized instruments under magnification.
Tinnitus (Ringing in the Ears)
- Treatment of Underlying Causes: Managing underlying conditions contributing to tinnitus, such as hearing loss, ear infections, or vascular issues.
- Sound Therapy: Using devices that emit low-level background noise to mask the ringing sensation.
- Counseling: Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) or counseling to help individuals cope with tinnitus-related distress.
Clinic contact number: +989371200167
Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can result from various causes, including age-related changes, noise exposure, infections, genetics, and underlying medical conditions. Treatment options for hearing loss depend on the type and severity of the impairment. Here are common approaches to managing hearing loss:
Hearing Aids
Amplification devices designed to enhance hearing for individuals with sensorineural or conductive hearing loss.
Cochlear Implants
Surgical implants that stimulate the auditory nerve to bypass damaged parts of the inner ear, suitable for severe hearing loss.
Medications
Certain medications may be prescribed to treat hearing loss caused by specific medical conditions.
Vertigo or Dizziness
- Medications: Vestibular suppressants or anti-nausea medications to alleviate symptoms of vertigo.
- Vestibular Rehabilitation: Specific exercises and maneuvers aimed at improving balance and reducing dizziness.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding triggers such as caffeine, alcohol, and certain head movements that exacerbate vertigo.
Eardrum Perforation
- Observation: Small perforations may heal on their own without intervention, with close monitoring by an otolaryngologist.
- Tympanoplasty: Surgical repair of the eardrum using tissue grafts to close larger perforations and restore hearing function.
- Antibiotics: Prescribed to prevent or treat infections associated with eardrum perforations.
What Do Medical Ear Treatments Involve?
Medical ear treatments vary based on the specific condition being addressed. When an individual seeks medical attention for an ear problem, the first step involves a thorough examination of the ear by an Otorhinolaryngologist (ENT specialist). The ENT specialist will use an otoscope to inspect the ear canal, eardrum, and middle ear structures.
Otoplasty, also known as ear surgery or ear reshaping, is a cosmetic procedure designed to alter the ears’ size, shape, or position. It is a popular surgical option for individuals who are dissatisfied with the appearance of their ears or wish to correct birth defects or injuries.
If an infection is present, antibiotics or ear drops might be prescribed. Pain relievers can be recommended to manage discomfort. In cases of excessive earwax, the healthcare professional may remove it using gentle irrigation or specialized tools. For more complex issues, such as chronic infections or structural abnormalities, surgery might be necessary.
Advancements in Otology
Medical ear treatments, also known as otology, have seen significant advancements driven by renowned experts and institutions in the field of otolaryngology. Institutions like the House Ear Institute (now the House Clinic) and the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary have been at the forefront of otologic research and clinical care. Dr. William F. House, often considered the “Father of Neurotology,” pioneered cochlear implant technology and founded the House Ear Institute, which has contributed extensively to the development of medical ear treatments.
One of the most active hospitals specializing in medical ear treatments is the Cleveland Clinic, known for its Center for Neurological Restoration and comprehensive otology and neurotology programs. The clinic’s otolaryngologists and neurotologists perform advanced procedures such as cochlear implantation, tympanoplasty, and stapedectomy, addressing a wide range of ear-related conditions.
According to recent statistics from the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS), the demand for medical ear treatments has risen steadily over the past decade, with an increasing number of patients benefiting from innovative therapies and surgical interventions for hearing restoration and ear disorders. These advancements highlight the critical role of specialized medical ear treatments in improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
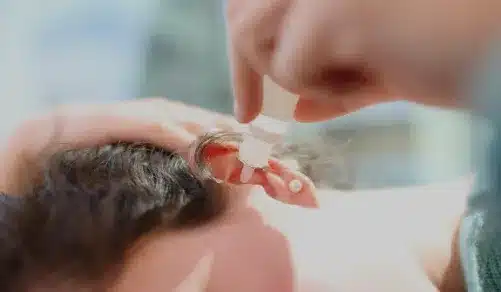
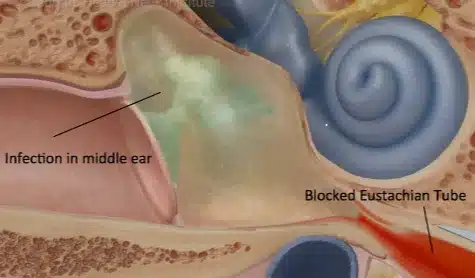
Ear Infections: Causes and Prevention
Ear infections occur when bacteria or viruses invade the middle ear, causing inflammation and fluid buildup. Common causes include respiratory infections, allergies, and exposure to water in the ear canal. Young children are particularly susceptible to ear infections due to their underdeveloped Eustachian tubes, which can lead to poor fluid drainage.
To prevent ear infections, maintaining good hygiene is essential. Avoid exposing the ears to excessive water and dry the ears thoroughly after swimming or bathing. It’s also important to manage allergies and promptly treat respiratory infections to minimize the risk of secondary ear infections.
Swimmer’s ear (also known as otitis externa) is a bacterial infection typically caused by water that stayed in the outer ear canal for a long period of time, providing a moist environment for bacteria to grow. CDC
Years of Study for Otorhinolaryngologists
Otorhinolaryngologists, also known as ENT specialists, undergo extensive medical training and education to specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of ear, nose, and throat disorders. After completing medical school, aspiring ENT specialists typically undertake a residency program in Otorhinolaryngology, which typically lasts for five to six years. This comprehensive training equips them with the necessary skills and knowledge to address a wide range of ear-related conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, medical ear treatments within the fields of otology, otolaryngology, and neurotology play a vital role in addressing a wide range of ear-related conditions and disorders. Otology focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of diseases affecting the ear, including hearing loss, infections, and structural issues within the intricate ear anatomy. Otolaryngologists specializing in otology and neurotology are equipped with specialized knowledge and skills to provide comprehensive care, utilizing advanced diagnostic techniques and surgical interventions to optimize ear health and restore auditory function.
The integration of neurotology into medical ear treatments further expands the scope of care to include disorders of the inner ear and vestibular system. Understanding the complexities of ear anatomy and neurosensory pathways enables otologists and neurotologists to tailor treatment strategies for each patient, emphasizing precision and patient-centered care. With ongoing advancements in technology and research, medical ear treatments continue to evolve, offering new possibilities for improving outcomes and enhancing the quality of life for individuals with ear-related conditions.
Clinic contact number: +989371200167
FAQs
- Can ear infections go away without treatment?
Some mild ear infections can resolve on their own, but it is generally advisable to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications.
2. Are ear treatments painful?
Most ear treatments are minimally invasive and do not cause significant pain. However, individual experiences may vary, and some procedures might cause mild discomfort.
3. What treatments are available for ear infections?
Treatment for ear infections often involves antibiotic ear drops or oral antibiotics to clear bacterial infections. Pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen may be recommended to manage ear pain and inflammation. In some cases, ear tubes may be needed for recurrent infections.
4. How are earwax blockages treated?
Earwax blockages can be treated by softening the wax with over-the-counter ear drops or using irrigation (ear syringing) to flush out the wax. In some cases, a healthcare provider may need to manually remove the earwax using specialized tools under magnification.
5. What options are available for hearing loss?
Treatment options for hearing loss depend on the cause and severity of the hearing impairment. They may include hearing aids, cochlear implants (for severe hearing loss), medications (for certain types of hearing loss), or surgical interventions to correct underlying structural issues.
Ear Infections | Healthy Swimming | Healthy Water | CDC