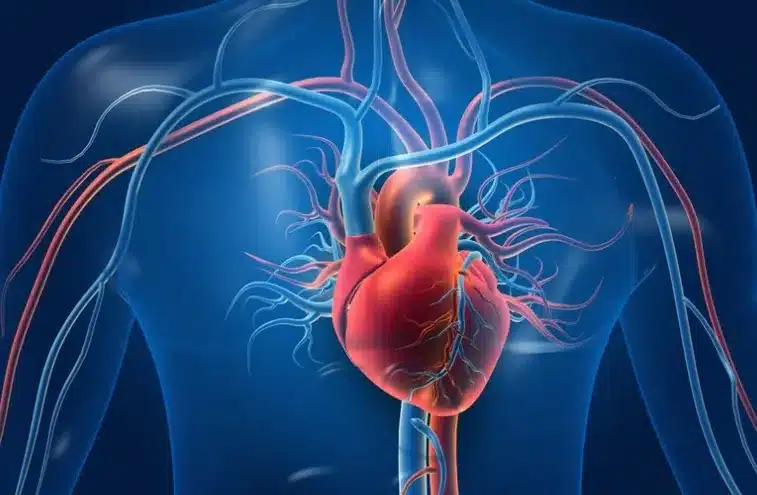
“Cardiothoracic surgery encompasses a specialized branch of medicine focusing on surgical procedures within the chest cavity. This field includes both heart surgery, addressing conditions within the heart, and thoracic surgery, involving interventions within the thoracic region. Procedures such as thymectomy, aimed at removing the thymus gland, exemplify the intricate and vital nature of cardiothoracic surgeries in treating a diverse range of conditions.”
History of Cardiology: A Journey through Time
The roots of cardiology can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where observations and rudimentary treatments of heart-related ailments were recorded. However, it was not until the 19th and 20th centuries that significant strides were made in understanding cardiac physiology and developing surgical interventions. Pioneers such as William Harvey, who described blood circulation, and Andreas Vesalius, who provided detailed anatomical insights, laid the foundation for modern cardiology.
Clinic contact number: +989371200167
What is Cardiology?
Cardiology is the branch of medicine dedicated to the study, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases and abnormalities of the heart. It encompasses non-invasive techniques, such as diagnostic imaging and stress testing, and invasive procedures, including angioplasty, stenting, and open-heart surgery. Cardiologists specialize in the prevention, management, and rehabilitation of cardiovascular conditions.
Types of Cardiothoracic Surgery
Cardiothoracic surgery encompasses a wide range of procedures, each tailored to address specific conditions. Some of the commonly performed surgeries include:
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): This procedure involves bypassing blocked or narrowed coronary arteries by grafting healthy blood vessels from other parts of the body.
- Valve Replacement/Repair: Damaged or diseased heart valves can be repaired or replaced with mechanical or biological substitutes to restore proper cardiac function.
- Aortic Aneurysm Repair: This surgery addresses the enlargement or weakening of the aorta, the body’s main blood vessel, by either replacing the affected segment or reinforcing it with a graft.
- Lung Resection: Removal of a portion or the entire lung is performed to treat lung cancer, infection, or certain lung conditions.
- Heart Transplantation: In severe cases of heart failure, a heart transplant may be the only viable treatment option. It involves replacing a failing heart with a healthy donor heart.
The Most Common Cardiothoracic Surgery
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is one of the most frequently performed cardiothoracic surgeries. This procedure is typically indicated for individuals with significant coronary artery disease, where the blood flow to the heart muscle is impaired. By bypassing the blocked arteries, CABG restores adequate blood supply to the heart, alleviating symptoms and reducing the risk of complications.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) is a surgical procedure used to bypass blocked or narrowed coronary arteries by grafting healthy blood vessels to improve blood flow to the heart.
Explanation
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a surgical procedure used to treat coronary artery disease (CAD), where the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked due to atherosclerosis (plaque buildup). CABG involves creating new pathways (bypass grafts) using healthy blood vessels from other parts of the body to bypass blocked or narrowed coronary arteries, allowing improved blood flow to the heart muscle.
Indications
CABG is recommended for patients with severe CAD who experience symptoms such as chest pain (angina) that cannot be adequately managed with medications or other treatments. It may also be performed in emergency situations, such as during a heart attack.
Procedure
During CABG, the surgeon makes an incision in the chest to access the heart. The patient is connected to a heart-lung bypass machine, which temporarily takes over the heart’s pumping function. The surgeon then grafts healthy blood vessels (usually from the leg, arm, or chest) onto the coronary arteries beyond the blockages, creating new routes for blood flow.
Recovery
Recovery from CABG involves a hospital stay of several days for monitoring and rehabilitation. Patients participate in cardiac rehabilitation programs to regain strength and endurance. Full recovery may take several weeks to months, depending on individual health and the extent of surgery.
Valve Replacement or Repair Surgery
Valve replacement or repair surgery involves replacing or modifying damaged heart valves to restore normal blood flow and cardiac function.
Explanation
Valve replacement or repair surgery is performed to treat heart valve disorders, such as aortic stenosis (narrowing of the aortic valve) or mitral regurgitation (leaky mitral valve). In valve replacement surgery, the diseased valve is replaced with a mechanical valve or a biological tissue valve (from animal or human tissue). Valve repair surgery aims to preserve the patient’s natural valve structure and function.
Indications
Valve replacement or repair surgery is recommended for patients with severe valve dysfunction that causes symptoms like shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, or heart failure. It may also be performed to prevent complications such as heart failure or stroke.
Procedure
During valve replacement surgery, the surgeon makes an incision in the chest to access the heart. The damaged valve is removed and replaced with a prosthetic valve. In valve repair surgery, the surgeon modifies the existing valve structure to improve its function.
Recovery
Recovery from valve surgery involves a hospital stay for monitoring and rehabilitation. Patients receive medications to prevent blood clots and infection. Cardiac rehabilitation programs help optimize recovery and restore heart function.
Thoracic (Lung) Surgery
Thoracic (lung) surgery encompasses procedures performed on the lungs and chest cavity, including lung resections for cancer, pleural interventions, and mediastinal surgeries.
Explanation
Thoracic surgery encompasses procedures performed on the lungs and other structures within the chest cavity. Common thoracic surgeries include lung resections (lobectomy or pneumonectomy) for lung cancer, surgical treatment of pleural effusions or infections, and procedures to diagnose and treat mediastinal tumors or abnormalities.
Indications
Thoracic surgery is indicated for conditions such as lung cancer, pulmonary nodules, pleural effusions, pneumothorax (collapsed lung), or mediastinal masses that require biopsy or surgical resection.
Procedure
Thoracic surgeries are performed using minimally invasive techniques (video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery or VATS) or traditional open approaches, depending on the specific condition and surgical goals. The surgeon makes incisions in the chest wall to access and treat the affected structures.
Clinic contact number: +989371200167
Recovery
Recovery from thoracic surgery varies depending on the procedure and individual health. Patients may require chest tube drainage, respiratory therapy, and pain management. Rehabilitation programs promote optimal lung function and overall recovery.
The Involvement of Cardiology in Surgical Interventions
Cardiology plays a crucial role in cardiothoracic surgery by providing a comprehensive assessment of a patient’s cardiac health before, during, and after the procedure. Cardiologists work closely with cardiothoracic surgeons to optimize patients’ cardiovascular status, monitor cardiac function during surgery, and manage postoperative care. Their expertise in diagnostic imaging, electrophysiology, and interventional procedures significantly contributes to successful outcomes in cardiothoracic surgeries.
Cardiac Electrophysiology: Unraveling the Heart’s Electrical System
Cardiac electrophysiology focuses on the electrical properties and rhythms of the heart. It involves the study and treatment of conditions such as arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms) and conduction abnormalities. Electrophysiologists utilize specialized techniques, including catheter ablation and implantation of pacemakers or defibrillators, to restore normal cardiac rhythm and improve patients’ quality of life.
Cardiothoracic surgeons operate on some of the most vital organs in your body. The surgeries they do are often complex. Be sure to ask your surgeon questions about anything you don’t understand about your surgery. Cleveland Clinic
Types of Heart Surgeries
In addition to CABG, various other heart surgeries are performed to address specific cardiac conditions. These include:
- Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) Repair: Corrects a hole in the wall separating the heart’s upper chambers (atria).
- Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Repair: Fixes a hole in the wall dividing the heart’s lower chambers (ventricles).
- Ablation Procedures: Destroys abnormal heart tissue causing arrhythmias through catheter-based techniques.
- Mitral Valve Repair/Replacement: Treats malfunctioning mitral valves, which regulate blood flow between the heart’s left atrium and left ventricle.
- Trans myocardial Laser Revascularization (TMR): Enhances blood flow to the heart by creating channels using laser energy.
10 Risks of Cardiothoracic Surgery
While cardiothoracic surgery has transformed the lives of countless patients, it is not without risks. The following are some potential complications associated with these procedures:
- Infection at the surgical site
- Bleeding or blood clots
- Adverse reactions to anesthesia
- Irregular heart rhythms
- Stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- Kidney dysfunction
- Lung problems, such as pneumonia or collapsed lung.
- Wound healing issues
- Allergic reactions
- Death (although rare)
It is important to note that the specific risks and outcomes vary depending on the individual patient, the procedure performed, and other contributing factors.
The Difference Between Cardiac Surgery and Cardiothoracic Surgery
The terms “cardiac surgery” and “cardiothoracic surgery” are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings. Cardiac surgery specifically refers to procedures performed on the heart and its blood vessels, whereas cardiothoracic surgery encompasses surgeries involving both the heart and the thoracic (chest) cavity, which includes the lungs, esophagus, and other thoracic organs.
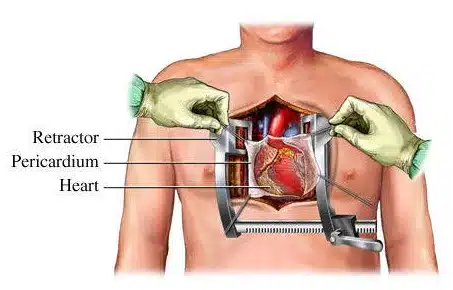
What Should I Expect During Recovery
During the recovery period after cardiothoracic surgery, it is essential to understand that each patient’s experience may vary. However, here are some general expectations and considerations:
- Hospital Stay: You will typically spend a few days after surgery. Your stay duration depends on the procedure performed and your overall health.
- Pain Management: Pain and discomfort are joint after surgery. Your healthcare team will provide appropriate pain medications to keep you comfortable. Communicate any pain levels or concerns to your healthcare providers.
The Evolution of Cardiothoracic Surgery
Cardiothoracic surgery, encompassing procedures on the heart and chest, is a highly specialized field marked by significant contributions from prestigious institutions and individuals. Prominent universities such as Johns Hopkins University and Mayo Clinic are leaders in training specialists in this area. Renowned figures in the field include Michael DeBakey and Magdi Yacoub, who have made substantial advancements in surgical techniques and patient care.
In recent years, Cleveland Clinic has emerged as one of the most active hospitals in the realm of cardiothoracic surgery, frequently leading in volumes of complex procedures and patient outcomes. Industry statistics indicate a steady increase in the number of surgeries performed, with technological advancements like minimally invasive surgical techniques and robotic-assisted thoracic surgery enhancing success rates and reducing recovery times. These innovations highlight the dynamic nature of the field and its continuous evolution towards more efficient and less invasive treatments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cardiothoracic surgery stands as a cornerstone in the realm of surgical medicine, offering life-saving interventions for conditions affecting the heart and thoracic organs. Through heart surgery, intricate procedures like coronary artery bypass grafting and valve replacements restore cardiac function, prolonging and enhancing the lives of patients with cardiovascular diseases. Simultaneously, thoracic surgery addresses conditions such as lung cancer through procedures like lung resection and lobectomy, highlighting the versatility and breadth of expertise within the field.”
“Moreover, the advent of minimally invasive cardiac surgery has revolutionized treatment approaches, offering patients reduced pain, shorter recovery times, and improved outcomes compared to traditional open-heart procedures. As technology continues to advance, the future of cardiothoracic surgery holds promise for further innovation, enabling surgeons to tackle complex conditions with greater precision and effectiveness while minimizing patient discomfort and recovery periods.
Clinic contact number: +989371200167
FAQs
- How long does cardiothoracic surgery take?
The duration of cardiothoracic surgery varies depending on the complexity of the procedure. Some surgeries can be completed within a few hours, while others may require several hours or even multiple sessions.
2. Are there any non-surgical alternatives for cardiothoracic conditions?
While surgery is often the most effective treatment option, non-surgical alternatives, such as medication, lifestyle modifications, and interventional cardiology procedures (e.g., angioplasty), may be appropriate for certain conditions. It is best to consult with a cardiologist to determine the most suitable approach for individual cases.
3. What are the different types of cardiothoracic surgeries? Common types of cardiothoracic surgeries include coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), heart valve repair or replacement, thoracic aortic surgery, lung resection (lobectomy or pneumonectomy), minimally invasive heart surgery, and esophageal surgeries.
4. When is cardiothoracic surgery recommended? Cardiothoracic surgery is recommended for patients with serious heart or lung conditions that have not responded well to conservative treatments like medications or lifestyle changes. It may also be used to repair congenital heart defects or treat certain cancers.
5. How is cardiothoracic surgery performed? Cardiothoracic surgeries can be performed using open techniques (traditional surgery with large incisions) or minimally invasive approaches (smaller incisions and specialized instruments). Procedures may involve using heart-lung bypass machines, robotic-assisted tools, or thoracoscopic cameras.
What Is a Cardiothoracic Surgeon? (clevelandclinic.org)